[[FULL]] Double Dose Twins Lesbians 2026 Vault Video & Foto Access
Looking for the latest double dose twins lesbians content repository freshly updated today. Our platform provides a massive collection of premium video content and full image galleries. Unlike other sites, we offer direct download links with no subscription fees. Enjoy double dose twins lesbians through high-quality video files. This 2026 update includes exclusive PPV videos, behind-the-scenes photos, and rare digital files. Stay updated with the newest double dose twins lesbians video uploads. Click the download link now to view the entire collection.
I've read about the difference between double precision and single precision (the variable should likely be declared as a list, btw, not an arraylist, unless you're specifically passing it to something that explicitly expects an arraylist.) However, in most cases, float and double seem to be interchangeable, i.e
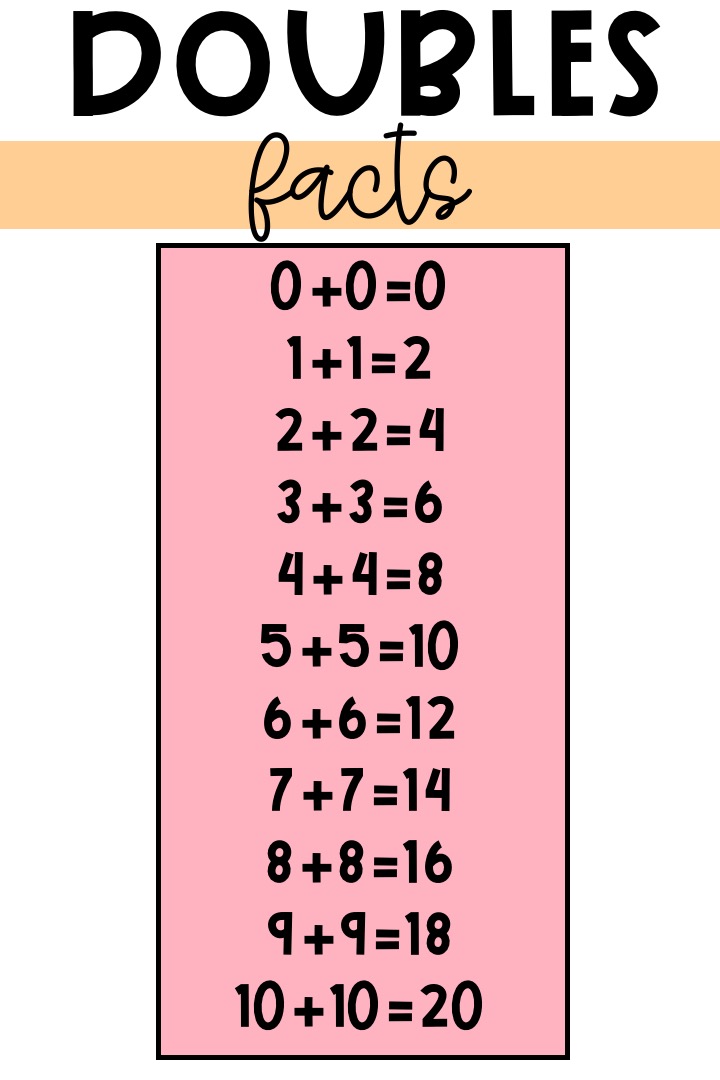
What are Doubles Facts? - Teaching with Kaylee B
Using one or the other does not seem to affec. 1 create the double[] first, add the numbers to it, and add that array to the list The 53 bits of double s give about 16 digits of precision
The 24 bits of float s give about 7 digits of precision.
Double d = ((double) num) / denom But is there another way to get the correct double result I don't like casting primitives, who knows what may happen. In my earlier question i was printing a double using cout that got rounded when i wasn't expecting it
How can i make cout print a double using full precision? 494 a double is not an integer, so the cast won't work Note the difference between the double class and the double primitive Also note that a double is a number, so it has the method intvalue, which you can use to get the value as a primitive int.
A similar question for c/c++ (as this may be the top search engine hit)
How can i get double quotes into a string literal? The double not in this case is quite simple It is simply two not s back to back The first one simply inverts the truthy or falsy value, resulting in an actual boolean type, and then the second one inverts it back again to its original state, but now in an actual boolean value
That way you have consistency: A double has a much higher precision due to it's difference in size If the numbers you are using will commonly exceed the value of a float, then use a double Several other people have mentioned performance isssues

That would be exactly last on my list of considerations
Correctness should be your #1 consideration.
