【MEGA】 Ester Bron Only Fans Full Collection HD Media Access
Browse the private ester bron only fans content repository updated for 2026. Our platform provides a massive collection of high-definition videos, private photos, and unreleased files. To ensure the best experience, get direct download links with no subscription fees. See ester bron only fans in stunning 4K clarity. Our latest January folder contains unseen video clips, leaked image sets, and full creator archives. Get the freshest ester bron only fans media drops. Click the download link now to unlock the premium gallery.
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (h) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group (−oh) of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (r ′) The names for esters include prefixes that denote the lengths of the carbon chains in the molecules and are derived following nomenclature rules similar to those for inorganic acids and salts. [1] these compounds contain a distinctive functional group.
Ester Molecule
Ester, any of a class of organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols and organic or inorganic acids In an ester, the second oxygen atom bonds to another carbon atom (figure 25.5a.) Esters derived from carboxylic acids are the most common
Learn about the different types and reactions of esters and more in this article.
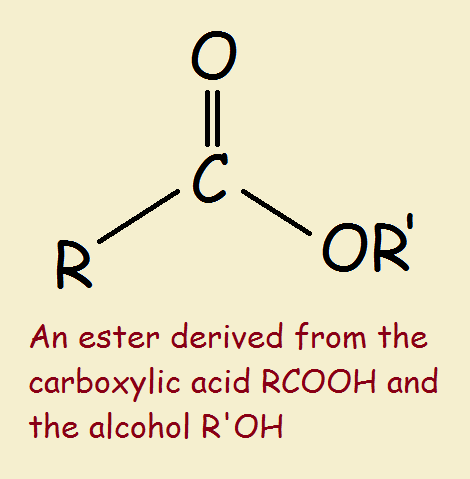
The general structure of an ester is rcoor', where r and r' represent alkyl or aryl groups Esters are derived from the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, resulting in the elimination of water. An ester is an organic compound where the hydrogen in the compound's carboxyl group is replaced with a hydrocarbon group Esters are derived from carboxylic acids and (usually) alcohol.
Key takeaway an ester has an or group attached to the carbon atom of a carbonyl group. In this tutorial you will learn about the basic properties and structure of an ester functional group You will also learn about esterification and its mechanism. The meaning of ester is any of a class of often fragrant organic compounds that can be represented by the formula rcoor' and that are usually formed by the reaction between an acid and an alcohol with elimination of water.
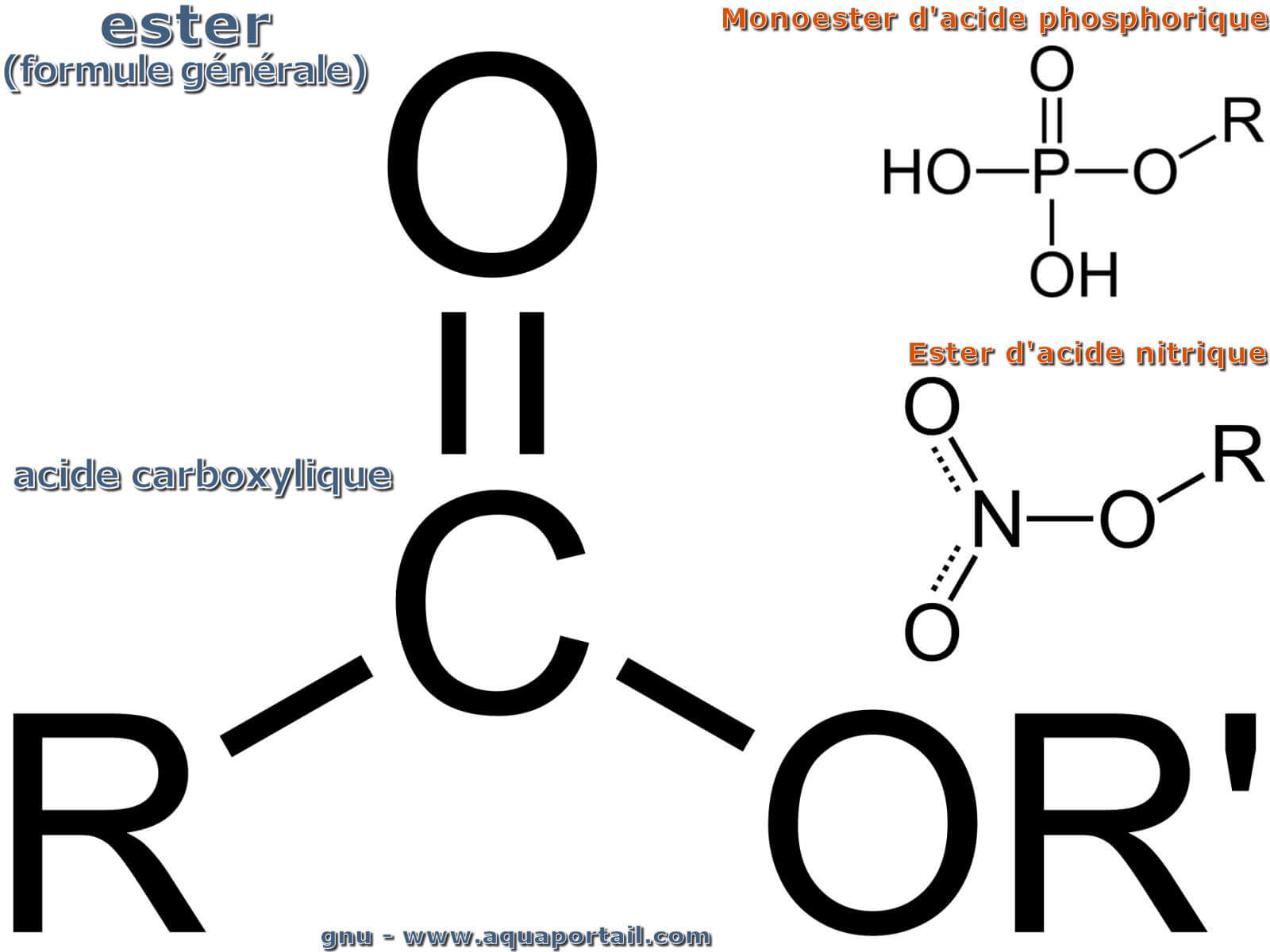
This could be an alkyl group like methyl or ethyl, or one containing a benzene ring like phenyl.
The ester linkage is also present in animal fats and in many biologically important molecules The chemical industry uses esters for a variety of purposes Ethyl acetate, for instance, is a commonly used solvent, and dialkyl phthalates are used as plasticizers to keep polymers from becoming brittle.
/ester-59134cd83df78c9283519859.png)