⦗HOT⦘ Leaking Amniotic Fluid At 33 Weeks 2026 Storage Full Media Access
Get exclusive access to the leaking amniotic fluid at 33 weeks content repository released in January 2026. Inside, you will find a huge library of 4K video sets, high-res images, and exclusive media clips. Unlike other sites, we offer one-click media downloads without any hidden costs. Watch leaking amniotic fluid at 33 weeks in stunning 4K clarity. Our latest January folder contains unseen video clips, leaked image sets, and full creator archives. Don't miss out on the latest leaking amniotic fluid at 33 weeks media drops. Access the full folder today to view the entire collection.
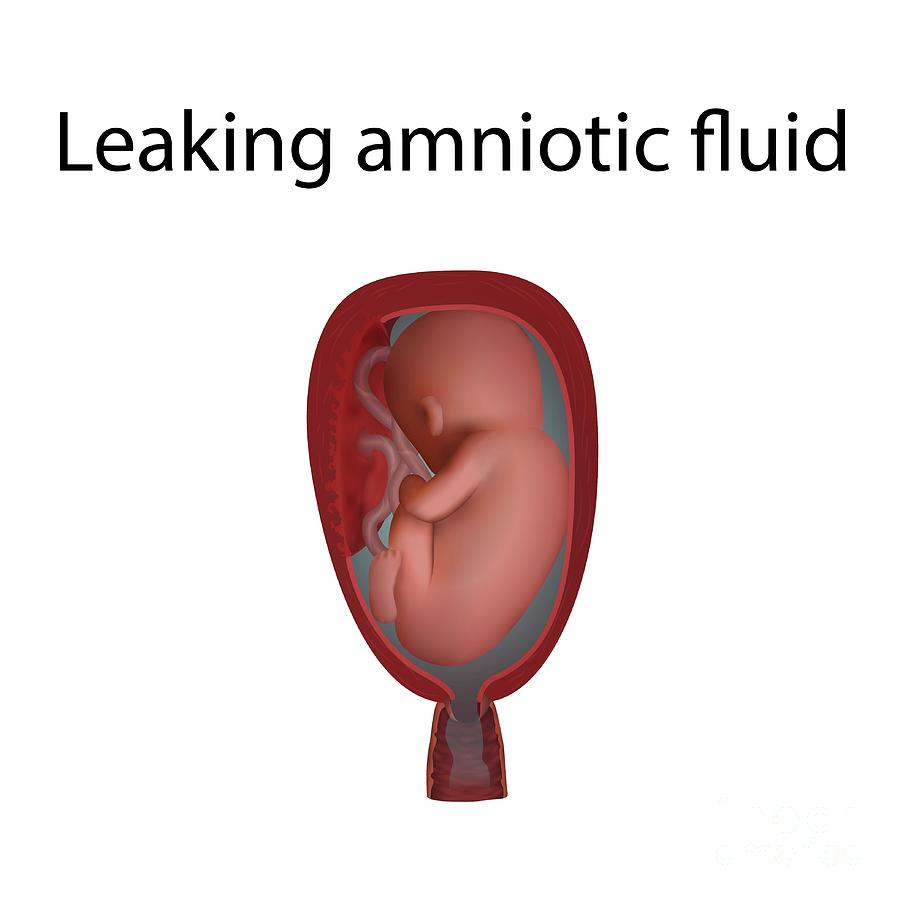
Leaking amniotic fluid toward the end of pregnancy is often a sign of labor The amount of amniotic fluid cushioning your baby tends to increase as your pregnancy progresses, reaching its highest point at about 36 weeks. 1 amniotic fluid is the fluid that surrounds a fetus during pregnancy
Leaking Amniotic Fluid, Oligohydramnios, and Birth Injury
When the amniotic sac breaks, known as the rupture of membranes (water breaking), you may feel a gush or trickle of warm liquid from the vagina. What’s considered a normal level of amniotic fluid Could i be leaking amniotic fluid
Yes, it's possible that during pregnancy your amniotic sac could break and leak amniotic fluid before you're in labor
If that happens, you have one of these conditions Prom stands for premature rupture of membranes, also called prelabor rupture of membranes How do you know if you’re leaking amniotic fluid It’s generally a gush but can start as a slow drip or leak
Read on to learn the signs of leaking amniotic fluid. Leaking fluid at 33 weeks often signals amniotic fluid loss, requiring prompt medical evaluation to ensure maternal and fetal safety. Premature rupture of membranes (prom) is when you leak amniotic fluid before labor begins It’s commonly called your “water breaking.” if it happens after 37 weeks of pregnancy, your provider delivers your baby

If it happens earlier, your provider weighs the risk of premature birth against the risks of complications such as infection.