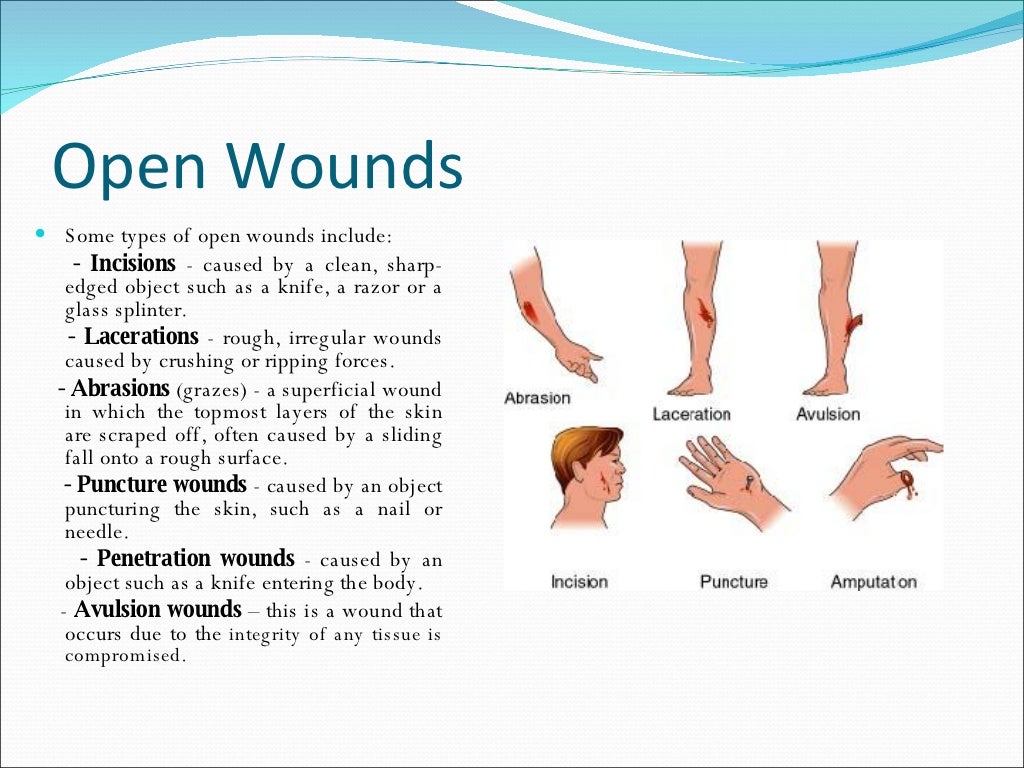
[[FULL]] Wound Leaking Clear Fluid Full Files Video & Foto Instant
Get exclusive access to the wound leaking clear fluid content repository freshly updated today. We offer the most complete database of high-definition videos, private photos, and unreleased files. For your convenience, we provide instant file access completely free for our community. Enjoy wound leaking clear fluid in stunning 4K clarity. The current media pack features exclusive PPV videos, behind-the-scenes photos, and rare digital files. Get the freshest wound leaking clear fluid media drops. Start your fast download immediately to save the files to your device.
Our goal is to heal your wound faster Our experienced wound care specialists in charleston, sc, provide advanced, compassionate care for chronic and nonhealing wounds and burns. We work with specialty wound care pharmacies, home health, and insurance so that each patient has the resources needed to heal.
Wound Care: A Guide to Practice for Healthcare Professionals
Wounds can be broadly classified as either acute or chronic based on time from initial injury and progression through normal stages of wound healing Depending on the cause, site and depth, a wound can range from simple to life threatening. Both wound types can further be categorized by cause of injury, wound severity/depth, and sterility of the wound bed.
The meaning of wound is an injury to the body (as from violence, accident, or surgery) that typically involves laceration or breaking of a membrane (such as the skin) and usually damage to underlying tissues.
A damaged area of the body, such as a cut or hole in the skin or flesh made by a weapon Wound, a break in the continuity of any bodily tissue due to an external action, typified by a cut, a bruise, or a hematoma. Learn essential skin wound treatment steps, from first aid care to recognizing when cuts need medical attention and stitches. Wounds are generally classified as open or closed
Both open and closed wounds often result in bleeding Open wounds may cause external bleeding, internal bleeding, or both Closed wounds may cause internal bleeding. An injury, usually involving division of tissue or rupture of the integument or mucous membrane, due to external violence or some mechanical agency rather than disease.
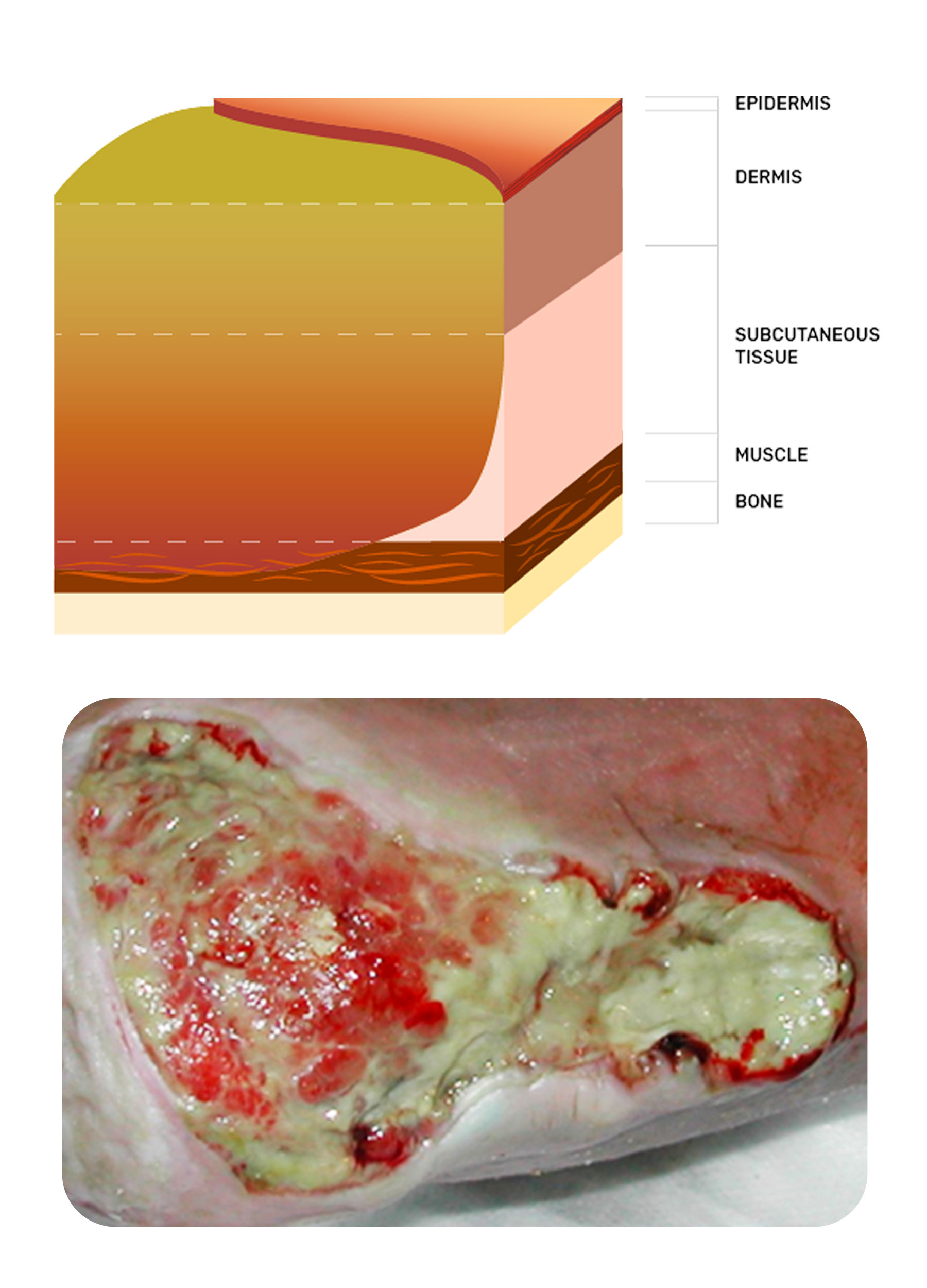
Most common wounds are superficial, limited to the outer skin layers, while some reach the deeper tissues and organs
![Wound Documentation [+ Free Cheat Sheet] | Lecturio](https://cdn.lecturio.com/assets/Nursing_CS_Wound-Types.jpg)